以出院病歷要來說, 為了管理大量的電子病歷,增加資料存取的速度,可以借助Oracle Partitioning機制,來達到上列的需求。 要決定要做Partitioning Table的欄位,就整份文件來看,以文件列印日期可以做為Table Partitioning Key。 XML node: /ClinicalDocument/effectiveTime 的 value 屬性. 重點是namespace的宣告
XML Type的表格,可以以XML欄位的內容,定義虛擬欄位
CREATE TABLE CDA_DOCS OF XMLType
XMLTYPE STORE AS BINARY XML
VIRTUAL COLUMNS
(DATE_COL AS (XMLCast(XMLQuery('declare default element namespace "urn:hl7-org:v3"; (: :)
declare namespace voc="http://www.hl7.org/v3/voc"; (: :)
declare namespace xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"; (: :)
/ClinicalDocument/effectiveTime/@value' PASSING OBJECT_VALUE RETURNING CONTENT)
AS varchar2(12))));
insert into CDA_DOCS select cda from XML_DOCS;
commit;
SELECT DATE_COL FROM CDA_DOCS;
Thursday, December 23, 2010
Tuesday, December 21, 2010
RAC ASM with EVA Business Copy
Install Oracle Clusterware and RAC
To create an additional disk group using ASMCA:
1. Prepare the disks or devices for use with ASM, as described in "Configuring
Installation Directories and Shared Storage" on page 2-17.
2. Start the Automatic Storage Configuration Assistant (ASMCA) from the Grid
home:
/u01/grid/bin/asmca
The ASM Configuration Assistant starts, and displays the Disk Groups window.
3. Click the Create button at the bottom left-hand side of the window to create a new
disk group.
The Create Disk Group window appears.
4. Provide the following information:
■ In the Disk Group Name field, enter a name for the new disk group, for
example, FRA.
■ Choose a Redundancy level, for example, Normal.
■ Select the disks to include in the new disk group.
If you used ASMLIB to configure the disks for use with ASM, then the
available disks are displayed if you have the Show Eligible option selected,
and they have a Header Status of PROVISIONED.
After you have provided all the information, click OK. A progress window titled
DiskGroup: Creation appears. After a few minutes, a message appears indicating
the disk group was created successfully. Click OK to continue.
5. Repeat Step 3 and 4 to create additional disk groups, or click Exit, then select Yes
to exit the utility.
Using Oracle Universal Installer to Install Oracle RAC
After you have configured the operating system environment, you can use Oracle
Universal Installer to install the Oracle Database software and create an Oracle RAC
database.
To install Oracle Database software on your cluster and create a clustered
database:
1. As the oracle user, use the following commands to start OUI, where
staging_area is the location of the staging area on disk, or the location of the
mounted installation disk:
cd /staging_area
./runInstaller
<Case I> directly recovery from EVA/BC S-Vols to P-Vols
1. shutdown ASM/RAC/CRS on fgodb03m and fgodb04m
2. un-present all BC/S-Vols from fgodb03m and fgodb04m
3. EVA/BC restore mirrorclone from S-Vols to P-Vols
4. after completed restored, then “fractured” all S-Vols
5. startup ASM/RAC/CRS on fgodb03m and fgodb04m
<Case II> directly startup ASM/RAC/CRS from EVA/BC S-Vols
To create an additional disk group using ASMCA:
1. Prepare the disks or devices for use with ASM, as described in "Configuring
Installation Directories and Shared Storage" on page 2-17.
2. Start the Automatic Storage Configuration Assistant (ASMCA) from the Grid
home:
/u01/grid/bin/asmca
The ASM Configuration Assistant starts, and displays the Disk Groups window.
3. Click the Create button at the bottom left-hand side of the window to create a new
disk group.
The Create Disk Group window appears.
4. Provide the following information:
■ In the Disk Group Name field, enter a name for the new disk group, for
example, FRA.
■ Choose a Redundancy level, for example, Normal.
■ Select the disks to include in the new disk group.
If you used ASMLIB to configure the disks for use with ASM, then the
available disks are displayed if you have the Show Eligible option selected,
and they have a Header Status of PROVISIONED.
After you have provided all the information, click OK. A progress window titled
DiskGroup: Creation appears. After a few minutes, a message appears indicating
the disk group was created successfully. Click OK to continue.
5. Repeat Step 3 and 4 to create additional disk groups, or click Exit, then select Yes
to exit the utility.
Using Oracle Universal Installer to Install Oracle RAC
After you have configured the operating system environment, you can use Oracle
Universal Installer to install the Oracle Database software and create an Oracle RAC
database.
To install Oracle Database software on your cluster and create a clustered
database:
1. As the oracle user, use the following commands to start OUI, where
staging_area is the location of the staging area on disk, or the location of the
mounted installation disk:
cd /staging_area
./runInstaller
<Case I> directly recovery from EVA/BC S-Vols to P-Vols
1. shutdown ASM/RAC/CRS on fgodb03m and fgodb04m
2. un-present all BC/S-Vols from fgodb03m and fgodb04m
3. EVA/BC restore mirrorclone from S-Vols to P-Vols
4. after completed restored, then “fractured” all S-Vols
5. startup ASM/RAC/CRS on fgodb03m and fgodb04m
<Case II> directly startup ASM/RAC/CRS from EVA/BC S-Vols
1. ASM/RAC/CRS online mode, EVA/BC re-sync from P-Vols to S-Vols
2. fgodb03m# su – oracle
3. fgodb03m> run_begin_backup.sh (enable begin backup mode)
4. “fractured” all S-Vols
5. fgodb03m> run_end_backup.sh (end of backup mode)
6. present all BC/S-Vols to fgodb03m and fgodb04m
7. #ioscan –f (on fgodb03m and fgodb04m)
8. #insf –e (on fgodb03m and fgodb04m)
Vdisks WWW | fgodb03m diskname | fgodb04m diskname | Old ASM diskname |
00dd (asm using) | disk66 (c?t1d3) (new asm) | disk61 (c?t1d3) (new asm) | disk38 (grid:asmoper) |
00c9 | disk71 (c?t1d4) | disk66 (c?t1d4) | disk33 |
00cc | disk75 (c?t1d5) | disk71 (c?t1d5) | disk34 |
00d1 | disk79 (c?t1d6) | disk75 (c?t1d6) | disk35 |
00d4 | disk86 (c?t1d7) | disk79 (c?t1d7) | disk36 |
9. fgodb03m#cd /dev/rdisk/
10. fgodb03m #chown grid:asmoper disk66 disk71 disk75 disk79 disk86
11. fgodb03m #chmod 664 disk66 disk71 disk75 disk79 disk86
12. fgodb04m#cd /dev/rdisk/
13. fgodb04m #chown grid:asmoper disk61 disk66 disk71 disk75 disk79
14. fgodb04m #chmod 664 disk61 disk66 disk71 disk75 disk79
15. shutdown ASM/RAC/CRS on fgodb03m and fgodb04m
16. chown bin:sys /dev/rdisk/disk38 (asm) on fgodb03m and fgodb04m
17. login as root on each nodes (fgodb03m,fgodb04m)
18. change directory to $GRID_HOME/bin (/opt/oracle/grid/bin)
19. run “#./crsctl start crs –excl”; “#./crsctl stop crs –f” on each nodes (fgodb03m run 1st , after done then run on fgodb04m) (./crsctl start crs –excl help ASM to find OCR and Voting disks)
20. root@fgodb03m:/opt/oracle/grid/bin#./crsctl query css votedisk
21. login as oracle and connect to ideal database instance
22. SQL> startup mount
23. SQL> alter database end backup;
24. SQL> shutdown immediate
25. start all crs and database resources
26. #./crsctl start crs (on each nodes fgodb03m,fgodb04m)
27. #./crsctl start resource -all
Run GDAL on Oracle Enterprise Linux
How to recompile GDAL reference document
Load I0022461-WGS84.GRE.ers into raster_table FIRST time (create a raster_table and column)
gdal_translate -of georaster I0022461-WGS84.BLU.ers georaster:scott/tiger,,raster_table,raster \
> -co "DESCRIPTION=(image_name varchar2(45), raster MDSYS.SDO_GEORASTER)" \
> -co "INSERT=VALUES('I0022461-WGS84.BLU',SDO_GEOR.INIT())" \
> -co "INTERLEAVE=BAND" -co "SRID=8307"
Load two more raster files into same table
gdal_translate -of georaster I0022461-WGS84.GRE.ers georaster:scott/tiger,,raster_table,raster \
-co "INSERT=VALUES('I0022461-WGS84.GRE',SDO_GEOR.INIT('RDT_1$', 3))" \
-co "INTERLEAVE=BAND" -co "SRID=8307"
gdal_translate -of georaster I0022461-WGS84.RED.ers georaster:scott/tiger,,raster_table,raster \
-co "INSERT=VALUES('I0022461-WGS84.RED',SDO_GEOR.INIT('RDT_1$', 4))" \
-co "INTERLEAVE=BAND" -co "SRID=8307"
After load files, update Geometry Metadata
insert into USER_SDO_GEOM_METADATA values('RASTER_TABLE', 'RASTER.SPATIALEXTENT',
SDO_DIM_ARRAY(
SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('X', 119.214515610089, 119.794140610089, 0.005),
SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('Y', 23.1398648460264, 23.8549398460264, 0.005)
), 8307);
commit;
Create pyramids for all the rasters in the table
DECLARE
geor_v sdo_georaster;
status varchar2(20);
BEGIN
FOR r in (SELECT image_name FROM raster_table ORDER BY georid) LOOP
SELECT raster INTO geor_v
FROM raster_table
WHERE image_name = r.image_name
FOR UPDATE;
sdo_geor.generatePyramid(geor_v, 'resampling=NN');
UPDATE image_table
SET raster = geor_v
WHERE image_name = r.image_name;
COMMIT;
END LOOP;
END;
/
Create Spatial Index
create index raster_table_raster_sdo_extent
on raster_table(raster.spatialextent)
indextype
is mdsys.spatial_index;
Document reference URL http://http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-edition/gdal-howto-compile-linux-130782.txt?ssSourceSiteId=otncn
For GDAL
========
Make sure your $ORACLE_HOME environment variable is set. If it is, SDO_GEORASTER will automatically be part of the GDAL build.
http://trac.osgeo.org/gdal/
Click on BuildHints
Click on DownloadSource
click on http://download.osgeo.org/gdal
click on daily
stable is stable code, trunk is code under development (you choose which one you want to compile).
trunk may contain fixes to SDO_GEORASTER extension that are not in stable.
.gz files are source code for UNIX/Linux, .zip files are source code for Windows
Unzip the source
cd to top level directory of source tree
mkdir full_path_to_GDAL_INSTALL_directory/GDAL_INSTALL
Call configure. Backslash ('\') is the continuation character for a UNIX command line
./configure --help
./configure \
--prefix=full_path_to_GDAL_INSTALL_directory/GDAL_INSTALL \
--with-ecw=full_path_to_GDAL_INSTALL_directory/ECW_INSTALL
setenv LD_LIBRARY_PATH full_path_to_GDAL_INSTALL_directory/ECW_INSTALL/lib
make
make install
Add full_path_to_GDAL_INSTALL_directory/GDAL_INSTALL/bin to your path environent variable.
To test install, georaster should appear as one of the gdalinfo formats.
For example, run the gdalinfo command as follows:
gdalinfo --formats
-- ECW (rw): ERMapper Compressed Wavelets
-- GeoRaster (rw+): Oracle Spatial GeoRaster
Load I0022461-WGS84.GRE.ers into raster_table FIRST time (create a raster_table and column)
gdal_translate -of georaster I0022461-WGS84.BLU.ers georaster:scott/tiger,,raster_table,raster \
> -co "DESCRIPTION=(image_name varchar2(45), raster MDSYS.SDO_GEORASTER)" \
> -co "INSERT=VALUES('I0022461-WGS84.BLU',SDO_GEOR.INIT())" \
> -co "INTERLEAVE=BAND" -co "SRID=8307"
Load two more raster files into same table
gdal_translate -of georaster I0022461-WGS84.GRE.ers georaster:scott/tiger,,raster_table,raster \
-co "INSERT=VALUES('I0022461-WGS84.GRE',SDO_GEOR.INIT('RDT_1$', 3))" \
-co "INTERLEAVE=BAND" -co "SRID=8307"
gdal_translate -of georaster I0022461-WGS84.RED.ers georaster:scott/tiger,,raster_table,raster \
-co "INSERT=VALUES('I0022461-WGS84.RED',SDO_GEOR.INIT('RDT_1$', 4))" \
-co "INTERLEAVE=BAND" -co "SRID=8307"
After load files, update Geometry Metadata
insert into USER_SDO_GEOM_METADATA values('RASTER_TABLE', 'RASTER.SPATIALEXTENT',
SDO_DIM_ARRAY(
SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('X', 119.214515610089, 119.794140610089, 0.005),
SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('Y', 23.1398648460264, 23.8549398460264, 0.005)
), 8307);
commit;
Create pyramids for all the rasters in the table
DECLARE
geor_v sdo_georaster;
status varchar2(20);
BEGIN
FOR r in (SELECT image_name FROM raster_table ORDER BY georid) LOOP
SELECT raster INTO geor_v
FROM raster_table
WHERE image_name = r.image_name
FOR UPDATE;
sdo_geor.generatePyramid(geor_v, 'resampling=NN');
UPDATE image_table
SET raster = geor_v
WHERE image_name = r.image_name;
COMMIT;
END LOOP;
END;
/
Create Spatial Index
create index raster_table_raster_sdo_extent
on raster_table(raster.spatialextent)
indextype
is mdsys.spatial_index;
Monday, December 20, 2010
Loading XML Documents
電子病歷是一份XML格式的文件。傳統上都是檔案的型式儲存於檔案伺服器上管理,然後在關聯式資料庫表格,用"pointer"指向儲存的檔案位置。在安全與查詢(指針對文件內容)都有諸多限制。
Oracle 資料庫提供原生性的XML欄位格式,提供以XQuery或是SQL view的方式提供查詢XML文件內容。下列的指令, 是如何將XML文件放入Oracle資料庫的步驟
1. Create a XML table. (如何建立XML表格)
建立一個XML資料表格,我的意思是一 XML Table只有一個欄位, XMLType欄位。
This is easy. As a normal table creation but define a column which its data type is XMLType.
CREATE TABLE "CGMH"."XML_DOCS"
( "CDA" "SYS"."XMLTYPE"
) SEGMENT CREATION IMMEDIATE
PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255 NOCOMPRESS LOGGING
STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645
PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT CELL_FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT)
TABLESPACE "USERS"
XMLTYPE COLUMN "CDA" STORE AS BASICFILE BINARY XML (
TABLESPACE "USERS" ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192 PCTVERSION 10
CACHE READS LOGGING
STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645
PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT CELL_FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT)) ALLOW NONSCHEMA DISALLOW ANYSCHEMA ;
Oracle 資料庫提供原生性的XML欄位格式,提供以XQuery或是SQL view的方式提供查詢XML文件內容。下列的指令, 是如何將XML文件放入Oracle資料庫的步驟
1. Create a XML table. (如何建立XML表格)
建立一個XML資料表格,我的意思是一 XML Table只有一個欄位, XMLType欄位。
This is easy. As a normal table creation but define a column which its data type is XMLType.
CREATE TABLE "CGMH"."XML_DOCS"
( "CDA" "SYS"."XMLTYPE"
) SEGMENT CREATION IMMEDIATE
PCTFREE 10 PCTUSED 40 INITRANS 1 MAXTRANS 255 NOCOMPRESS LOGGING
STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645
PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT CELL_FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT)
TABLESPACE "USERS"
XMLTYPE COLUMN "CDA" STORE AS BASICFILE BINARY XML (
TABLESPACE "USERS" ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW CHUNK 8192 PCTVERSION 10
CACHE READS LOGGING
STORAGE(INITIAL 65536 NEXT 1048576 MINEXTENTS 1 MAXEXTENTS 2147483645
PCTINCREASE 0 FREELISTS 1 FREELIST GROUPS 1 BUFFER_POOL DEFAULT FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT CELL_FLASH_CACHE DEFAULT)) ALLOW NONSCHEMA DISALLOW ANYSCHEMA ;
2. Load XML documents into XML table(將 XML文件載入 XML Table)
透過"目錄路徑"的物件,指定上載XML文件所在的路徑。在這裏我們首先建立"XMLDIR"的目錄路徑物件;然後再使用XMLType 函式載入文件。
透過"目錄路徑"的物件,指定上載XML文件所在的路徑。在這裏我們首先建立"XMLDIR"的目錄路徑物件;然後再使用XMLType 函式載入文件。
Things to be noticed is the encoding. Or I will lost the characters in XML documents.
Login Oracle Database as system to create Directory(or check if any Directory are available to use)
SQL> create directory XMLDIR as '/u01/opt/XML';
SQL> create directory XMLDIR as '/u01/opt/XML';
SQL> grant read, write on directory XMLDIR to cgmh;
Login as a Database user to load XML documents
Login as a Database user to load XML documents
SQL> connect cgmh/cgmh
Connected.
SQL> select * from all_directories;
OWNER DIRECTORY_NAME
------------------------------ ------------------------------
DIRECTORY_PATH
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SYS XMLDIR
/u01/opt/XML
SQL> insert into XML_DOCS values
2 (XMLType(bfilename('XMLDIR', 'CDABig5Sample.xml'), nls_charset_id('ZHT16MSWIN950')));
1 row created.
SQL> insert into XML_DOCS values
2 (XMLType(bfilename('XMLDIR', 'CDASample.xml'), nls_charset_id('AL32UTF8')));
1 row created.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
Thursday, October 14, 2010
Loading DEM
1. Request partner to translate DEM data into X, Y, Z format. The filename called"tw20fix84.img_XYZ.txt"
2. Create Oracle Directory, PC_DATA, by system and grant read/write privieges to user, FSMS.
3. Create external table, rawtext.
4. Create a POINT constructor for convenience with default SRID 4326.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION point(
x NUMBER, y NUMBER, srid NUMBER DEFAULT 4326)
RETURN SDO_GEOMETRY
DETERMINISTIC
IS
BEGIN
RETURN SDO_GEOMETRY(2001, srid, SDO_POINT_TYPE(x, y, NULL), NULL, NULL);
END;
/
5. Create a table, DEM, with a SDO_GEOMETRY column, location.
CREATE TABLE DEM
(
X NUMBER
, Y NUMBER
, Z VARCHAR2(10)
, LOCATION MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY
);
6. Load data, rawtext, into table, DEM, by using insert select SQL.
INSERT INTO dem
SELECT x, y, z, point(x, y)
FROM rawtext;
7. Update USER_SDO_GEOM_METADATA
Before update SDO_GEOM_METADATA, I got to know the MBR
SELECT SDO_AGGR_MBR(location) FROM dem;
or for this , I use
SELECT MIN(x), MAX(x), MIN(y), MAX(y), MIN(z), MAX(z)
FROM dem;
MIN(X) MAX(X) MIN(Y) MAX(Y) MIN(Z) MAX(Z)
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
119.982565 122.02683 21.8673002 25.3523955 0 999
2. Create Oracle Directory, PC_DATA, by system and grant read/write privieges to user, FSMS.
3. Create external table, rawtext.
4. Create a POINT constructor for convenience with default SRID 4326.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION point(
x NUMBER, y NUMBER, srid NUMBER DEFAULT 4326)
RETURN SDO_GEOMETRY
DETERMINISTIC
IS
BEGIN
RETURN SDO_GEOMETRY(2001, srid, SDO_POINT_TYPE(x, y, NULL), NULL, NULL);
END;
/
5. Create a table, DEM, with a SDO_GEOMETRY column, location.
CREATE TABLE DEM
(
X NUMBER
, Y NUMBER
, Z VARCHAR2(10)
, LOCATION MDSYS.SDO_GEOMETRY
);
6. Load data, rawtext, into table, DEM, by using insert select SQL.
INSERT INTO dem
SELECT x, y, z, point(x, y)
FROM rawtext;
7. Update USER_SDO_GEOM_METADATA
Before update SDO_GEOM_METADATA, I got to know the MBR
SELECT SDO_AGGR_MBR(location) FROM dem;
or for this , I use
SELECT MIN(x), MAX(x), MIN(y), MAX(y), MIN(z), MAX(z)
FROM dem;
MIN(X) MAX(X) MIN(Y) MAX(Y) MIN(Z) MAX(Z)
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
119.982565 122.02683 21.8673002 25.3523955 0 999
Use this information to update USER_SDO_GEOM_METADATA
INSERT INTO
USER_SDO_GEOM_METADATA
VALUES (
'DEM','LOCATION',
SDO_DIM_ARRAY(SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('X',119.982565,122.02683,10),
SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('Y',21.8673002,25.3523955,10)
),4326);
8. Now, it's time to create spatial index
CREATE INDEX sdo_dem_location ON dem (location)
INDEXTYPE IS MDSYS.SPATIAL_INDEX;
Then we can perform some queries.
Sunday, October 10, 2010
Taiwan Coordinate System in Oracle Spatial
As updated by NetGeo. We should use SRID=4326 in Oracle Spatial. It is Geodetic2D coordinate system.
Wednesday, September 29, 2010
Using SDO_PC_PKG
Create a global temporary table for multi users
create global temporary table queryres as select * from MDSYS.sdo_pc_blk_table;
Q1: Give any point(x,y), how to get the Z-axis?
SDO_Geometry Point constructor:
sdo_geometry(2001,26910, sdo_point_type(532895.65,4276546.48,null),NULL,NULL)
Base on the point to create +/- tolerance MBR:
sdo_geometry(2003,26910, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1,1003,3), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY(532895.15,4276545.98,532896.15,4276546.98))
DECLARE
inp sdo_pc;
BEGIN
select pc into inp from pc_tab;
insert into queryres
select * from
table(sdo_pc_pkg.clip_pc
(inp,
END;
/
select sdo_pc_pkg.to_geometry(r.points, r.num_points,3,8307) from queryres r;
Q2: Clip an area
DECLARE
create global temporary table queryres as select * from MDSYS.sdo_pc_blk_table;
Q1: Give any point(x,y), how to get the Z-axis?
SDO_Geometry Point constructor:
sdo_geometry(2001,26910, sdo_point_type(532895.65,4276546.48,null),NULL,NULL)
Base on the point to create +/- tolerance MBR:
sdo_geometry(2003,26910, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1,1003,3), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY(532895.15,4276545.98,532896.15,4276546.98))
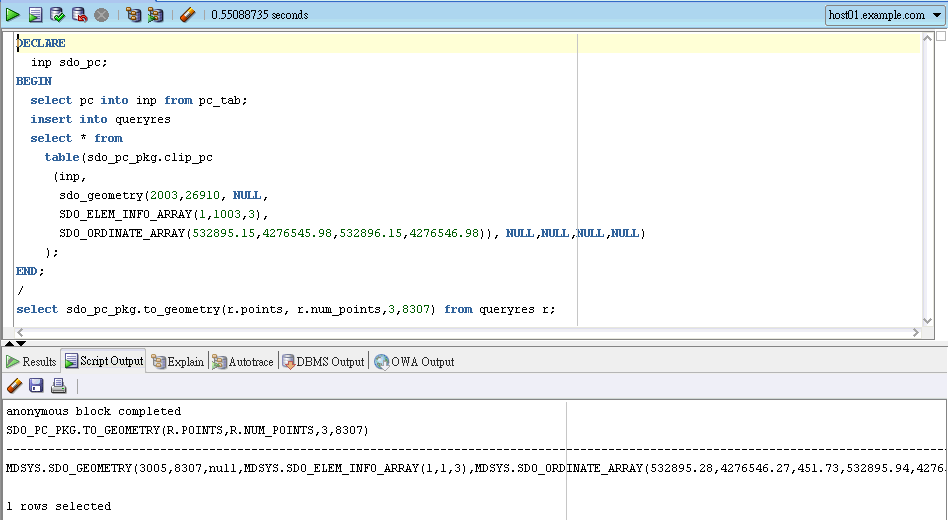
DECLARE
inp sdo_pc;
BEGIN
select pc into inp from pc_tab;
insert into queryres
select * from
table(sdo_pc_pkg.clip_pc
(inp,
sdo_geometry(2003,26910, NULL,
SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1,1003,3),
SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY(532895.15,4276545.98,532896.15,4276546.98)), NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL)
);
/
select sdo_pc_pkg.to_geometry(r.points, r.num_points,3,8307) from queryres r;
Q2: Clip an area
DECLARE
inp sdo_pc;
BEGIN
select pc into inp from pc_tab where rownum=1;
insert into queryres
select * from
table(sdo_pc_pkg.clip_pc
(inp,
sdo_geometry(2003,26910, NULL,
SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1,1003,3),
SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY(532000,4273000,532100,4273100)),NULL,NULL,NULL,NULL)
);
END;
/
select sdo_pc_pkg.to_geometry(r.points, r.num_points,3,8307) from queryres r;
Q3: For a line
Use SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER to create a line buffer, then run sdo_pc_pkg.clip_pc, and , sdo_pc_pkg.to_geometry
Monday, September 27, 2010
Update metadata in Oracle Dictionary & Creating Index
After upload Point Clouds into Oracle database. The next step is to update metadata. Let's check the Oracle dictionary.
select * from user_sdo_geom_metadata;
It looks great. Oracle automatic update the metadata after loading Point Clouds.
Check sdo_index:
select * from user_sdo_index_info;
That's really great. Oracle have done the update with the metadata and index.
select * from user_sdo_geom_metadata;
It looks great. Oracle automatic update the metadata after loading Point Clouds.
Check sdo_index:
select * from user_sdo_index_info;
That's really great. Oracle have done the update with the metadata and index.
Thursday, September 23, 2010
Following Appendix E Steps
1. Create table PC_TAB and add a SDO_PC column to store point cloud data
create table PC_TAB (pc SDO_PC);
2. Create PC_BLKTAB as the Block Table for the Point Cloud Data
create table PC_BLKTAB as select * from MDSYS.SDO_PC_BLK_TABLE;
3. Create INPTAB table storing Input Set of Points
CREATE SEQUENCE RID_SEQ INCREMENT BY 1 START WITH 1;
CREATE TABLE INPTAB( RID VARCHAR2(24), VAL_D1 NUMBER, VAL_D2 NUMBER, VAL_D3 NUMBER);
INSERT INTO inptab(rid, val_d1, val_d2, val_d3) SELECT RID_SEQ.NEXTVAL, X, Y, Z FROM points;
COMMIT;
4.Result Table for 3D Point Data
CREATE TABLE RESTAB ( PTN_ID NUMBER, POINT_ID NUMBER, RID VARCHAR2(24), VAL_D1 NUMBER, VAL_D2 NUMBER, VAL_D3 NUMBER);
5. Initializing, Inserting, and Populating a Point Cloud with an Input Set of Points
DECLARE
pc sdo_pc;
BEGIN
-- Initialize the point cloud object.
pc := sdo_pc_pkg.init(
'PC_TAB', -- Table that has SDO_PC column defined
'PC', -- Column name of SDO_PC object
'PC_BLKTAB', -- Table to store blocks of point cloud
'blk_capacity=5000', -- Using default setting
SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, 26910, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1,1003,3), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY(531159.776, 4272683.453, 534629.345, 4280409.657)), 0.0005, 3, NULL
);
-- Insert the point cloud object into the "base" table
INSERT INTO pc_tab (pc) VALUES (pc);
-- Create the blocks for the point cloud
sdo_pc_pkg.create_pc(
pc, --Initilized PointCloud object
'INPTAB', -- Name of input table to ingest into the point cloud
'RESTAB' -- Name of output table that stores the points
);
END;
/
PS. user who nneds
CONNECT, CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, CREATE INDEX, CREATE INDEXTYPE, CREATE SEQUENCE
create table PC_TAB (pc SDO_PC);
2. Create PC_BLKTAB as the Block Table for the Point Cloud Data
create table PC_BLKTAB as select * from MDSYS.SDO_PC_BLK_TABLE;
3. Create INPTAB table storing Input Set of Points
CREATE SEQUENCE RID_SEQ INCREMENT BY 1 START WITH 1;
CREATE TABLE INPTAB( RID VARCHAR2(24), VAL_D1 NUMBER, VAL_D2 NUMBER, VAL_D3 NUMBER);
INSERT INTO inptab(rid, val_d1, val_d2, val_d3) SELECT RID_SEQ.NEXTVAL, X, Y, Z FROM points;
COMMIT;
4.Result Table for 3D Point Data
CREATE TABLE RESTAB ( PTN_ID NUMBER, POINT_ID NUMBER, RID VARCHAR2(24), VAL_D1 NUMBER, VAL_D2 NUMBER, VAL_D3 NUMBER);
5. Initializing, Inserting, and Populating a Point Cloud with an Input Set of Points
DECLARE
pc sdo_pc;
BEGIN
-- Initialize the point cloud object.
pc := sdo_pc_pkg.init(
'PC_TAB', -- Table that has SDO_PC column defined
'PC', -- Column name of SDO_PC object
'PC_BLKTAB', -- Table to store blocks of point cloud
'blk_capacity=5000', -- Using default setting
SDO_GEOMETRY(2003, 26910, NULL, SDO_ELEM_INFO_ARRAY(1,1003,3), SDO_ORDINATE_ARRAY(531159.776, 4272683.453, 534629.345, 4280409.657)), 0.0005, 3, NULL
);
-- Insert the point cloud object into the "base" table
INSERT INTO pc_tab (pc) VALUES (pc);
-- Create the blocks for the point cloud
sdo_pc_pkg.create_pc(
pc, --Initilized PointCloud object
'INPTAB', -- Name of input table to ingest into the point cloud
'RESTAB' -- Name of output table that stores the points
);
END;
/
PS. user who nneds
CONNECT, CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, CREATE INDEX, CREATE INDEXTYPE, CREATE SEQUENCE
Wednesday, September 22, 2010
Prepare External Table for Loading Point Clouds
After down from data set from OpenTopography. I am interest in points.txt only when gz file was decompressed. Oracle Spatial User Developer Guide did not document well on how to load point cloud data set into Oracle database. Instead, I found the steps from "Pro Oracle Spatial for Oracle Database 11g" Appendix E.
I am going to create an external table link to points.txt as POINTS for loading points into Oracle SDO_PC data type. Before creating an external table, I need to create a directory, PC_DIR, and put point.tx on that directory.
Login as system to create PC_DIR.
create or replace directory "PC_DIR" as '/u01/opt/PC_dataset';
And grant READ & WRITE rights to user at least
grant read, write on directory PC_DIR to fsms;
Now I can create an external table.
CREATE TABLE "FSMS"."POINTS"
( "X" NUMBER,
"Y" NUMBER,
"Z" NUMBER,
"CLASSIFICATION" NUMBER,
"GPSTIME" NUMBER,
"SCAN_ANGLE" NUMBER,
"INTENSITY" NUMBER,
"NUMBER_OF_RETURNS" NUMBER,
"RETURN_NUMBER" NUMBER,
"POINT_SOURCE_ID" NUMBER,
"EDGE_OF_FLIGHT_LINE_FLAG" NUMBER,
"DIRECTION_OF_SCAN_FLAG" NUMBER,
"USER_DATA" NUMBER,
"RED_CHANNEL" NUMBER,
"GREEN_CHANNEL" NUMBER,
"BLUE_CHANNEL" NUMBER
)
ORGANIZATION EXTERNAL
( TYPE ORACLE_LOADER
DEFAULT DIRECTORY "PC_DIR"
LOCATION
( "PC_DIR":'points.txt'
)
)
REJECT LIMIT UNLIMITED;
Following the steps from Appendix E
I am going to create an external table link to points.txt as POINTS for loading points into Oracle SDO_PC data type. Before creating an external table, I need to create a directory, PC_DIR, and put point.tx on that directory.
Login as system to create PC_DIR.
create or replace directory "PC_DIR" as '/u01/opt/PC_dataset';
And grant READ & WRITE rights to user at least
grant read, write on directory PC_DIR to fsms;
Now I can create an external table.
CREATE TABLE "FSMS"."POINTS"
( "X" NUMBER,
"Y" NUMBER,
"Z" NUMBER,
"CLASSIFICATION" NUMBER,
"GPSTIME" NUMBER,
"SCAN_ANGLE" NUMBER,
"INTENSITY" NUMBER,
"NUMBER_OF_RETURNS" NUMBER,
"RETURN_NUMBER" NUMBER,
"POINT_SOURCE_ID" NUMBER,
"EDGE_OF_FLIGHT_LINE_FLAG" NUMBER,
"DIRECTION_OF_SCAN_FLAG" NUMBER,
"USER_DATA" NUMBER,
"RED_CHANNEL" NUMBER,
"GREEN_CHANNEL" NUMBER,
"BLUE_CHANNEL" NUMBER
)
ORGANIZATION EXTERNAL
( TYPE ORACLE_LOADER
DEFAULT DIRECTORY "PC_DIR"
LOCATION
( "PC_DIR":'points.txt'
)
)
REJECT LIMIT UNLIMITED;
Following the steps from Appendix E
Get the Point Cloud
In Taiwan, I really hard to get Point Cloud data set free. For test, I found I can get some data set from Open Topography (http://www.opentopography.org/).
Here is the metadata got from Open Topography. (it is around Napa where I had been visited a great restaurant, GrayStone).
The greatest thing for me is it clearly describes coordination:
Horizontal Coordinates: UTM Zone 10 N NAD83 Meters
Vertical Coordinates: Geoid89
...
Data Selection Coordinates:
Xmin: 531159.776
Xmax: 534629.345
Ymin: 4272683.453
Ymax: 4280409.657
Classifications: All
Base on Horizontal and Vertical Coordinates, I can query from Oracle Coordinates references table and decides which SRID I should choose.
So we got to choose SRID = 26910
Here is the metadata got from Open Topography. (it is around Napa where I had been visited a great restaurant, GrayStone).
The greatest thing for me is it clearly describes coordination:
Horizontal Coordinates: UTM Zone 10 N NAD83 Meters
Vertical Coordinates: Geoid89
...
Data Selection Coordinates:
Xmin: 531159.776
Xmax: 534629.345
Ymin: 4272683.453
Ymax: 4280409.657
Classifications: All
Base on Horizontal and Vertical Coordinates, I can query from Oracle Coordinates references table and decides which SRID I should choose.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)